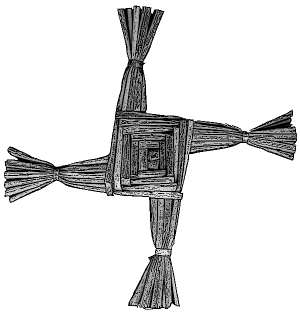
During the period of Christian conversion of Ireland in the 4th and 5th centuries, it was the strategy of monastic scholars to ensure an easy transition from Celtic to Christian belief. The disciples of Saint Patrick successfully deceived the Celts into thinking that the new faith of Rome was a mere extension of their traditional religion.
Christian missionaries incorporated elements of the peoples veneration of the Celtic Gods into Christian doctrine. The often used example of this religious shift is the fate of Brigid. Brigid was deftly transformed from a daughter of ‘The Dagda’ of the Tuatha Dé Danann into the Saint of the same name. In the early tales of the Christian Saint, Brigid is portrayed as the daughter of a Druidical household before her embrace of the new religion. The Druids were the priests of the pagan Celtic religion but were also akin to today’s upper middle classes: “The Druids were the professionals of pre Christian Celtic society. They comprised all the professions – doctors, lawyers, teachers, philosophers, ambassadors...(and priests of the Celtic Faith)” (Ellis). Thus with her conversion to Christianity, Brigid abandons the Celtic Gods and their priests, the Druids. To reinforce this transition the early church adopted the feast day of the Celtic Goddess Brigid, or Imbolg, to the feast day of the Christian saint.